UPDATE – The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has just released an update to their Computer Security Incident Handling Guide (SP 800-61). The guide contains very prescriptive guidance that can be used to frame, or enhance, your incident response plan. It also contains a very useful incident response checklist on page 42. I’ve taken the liberty of modifying it slightly to conform to the FFIEC guidance. It is form-fillable and available for download here. I hope you find it useful for testing purposes as well as actual incidents. I originally posted on this back in May 2012, here is the rest of the original post:
Although adherence to NIST standards is strictly required for Federal agencies, it is not binding for financial institutions. However NIST publications are referred to 10 times in the FFIEC IT Handbooks, 8 times in the Information Security Handbook alone. They are considered a best-practice metric by which you can measure your efforts. So because of…
- The importance of properly managing an information security event,
- The increasing frequency, complexity, and severity of security incidents,
- The scarcity of recent regulatory guidance in this area, and
- The relevance of NIST to future financial industry regulatory guidance,
…it should be required reading for all financial institutions.
Incident response is actually addressed in 4 FFIEC Handbooks; Information Security, Operations, BCP and E-Banking. It’s important to distinguish here between a security incident and a recovery, or business continuity, incident. This post will only address security incidents, but guidance states that the two areas intersect in this way:
“In the event of a security incident, management must decide how to properly protect information systems and confidential data while also maintaining business continuity.”
Security incidents and recovery incidents also share this in common…both require an impact analysis to prioritize the recovery effort.
So although there are several regulatory references to security incident management, none have been updated since 2008 even though the threat environment has certainly changed since then. Perhaps SP 800-61 will form the basis for this update just as SP 800-33 informed the FFIEC Information Security Handbook a few years after its release. But until it does, proactive Information Security Officers and Network Administrators would do well to familiarize (or re-familiarize) themselves with the basic concepts.
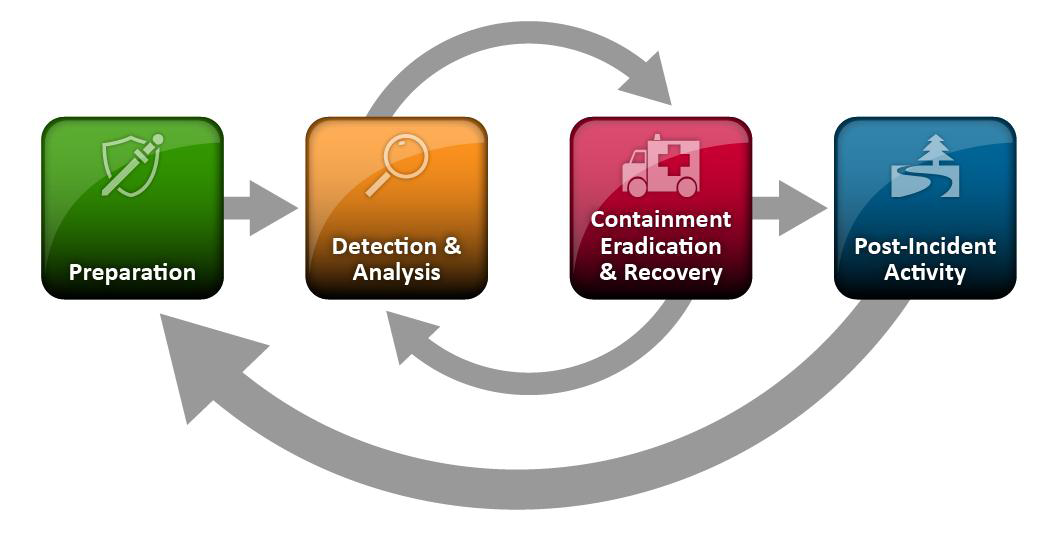
NIST defines the incident life-cycle this way:
Each section is detailed in the guide, and worth reading in its entirety, but to summarize:
- Preparation – Establish an incident response capability by defining a policy (typically part of your Information Security Program), and an incident response team (referred to in the FFIEC IT Handbook as the Computer Security Incident Response Team, or CSIRT). Smaller institutions may want to have the IT Steering Committee manage this. Assess the adequacy of your preventive capabilities in the current threat environment, including patch management, Anti-virus/Anti-malware, firewalls, network intrusion prevention and server intrusion prevention. Don’t forget employee awareness training…perhaps the most important preventive control.
- Detection & Analysis – Determine exactly what constitutes an incident, and under what circumstances you will activate your incident response team and initiate procedures. Signs of an incident fall into one of two categories: precursors and indicators. A precursor is a sign that an incident may occur in the future. An indicator is a sign that an incident may have occurred or may be occurring now. Many of the controls listed in the preparation phase (firewalls, IPS/IDS devices, etc.) can also alert to both precursors and indicators. The initial analysis should provide enough information for the team to prioritize subsequent activities, such as containment of the incident and deeper analysis of the effects of the incident (steps 3 & 4).
- Containment, Eradication & Recovery – Most incidents require containment to control and minimize the damage. An essential part of containment is decision-making i.e., shutting down a system, disconnecting it from a network, disabling certain functions, etc. Although you may be tempted to start the eradication and recovery phase immediately, bear in mind that you’ll need to collect as much forensic evidence as possible to facilitate the post-incident analysis.
- Post-Incident Activity – Simply put, lessons learned. It’s easy to ignore this step as you try to get back to the business of banking, but don’t. Some important questions to answer are:
- Exactly what happened, and at what times?
- How well did staff and management perform in dealing with the incident? Were the documented procedures followed? Were they adequate?
- Were any steps or actions taken that might have inhibited the recovery?
- What could we do differently the next time a similar incident occurs?
- What corrective actions can prevent similar incidents in the future?
- What additional tools or resources are needed to detect, analyze, and mitigate future incidents?
The FFIEC addresses intrusion response here, and recommends that “institutions should assess the adequacy of their preparations through testing.” Use the checklist, and recent security incidents to train your key CSIRT personnel, and then use the full guide to fine-tune and enhance your incident response capabilities.